Qu'est-ce que l'IPv6 ? Pourquoi choisissons-nous de l'utiliser ?
IPv6 was introduced to replace IPv4 and is often referred to as the “next generation Internet” because of its enhanced capabilities and its growth in recent years. IPv6 or Internet Protocol Version 6 is an upgrade of IPv4.

Why We Need IPv6
The challenges of IPv4
1. Lack of enough IP addresses
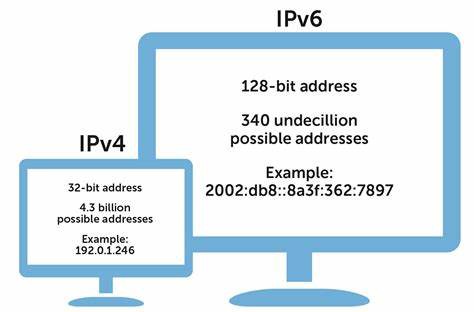
The earlier version, IPv4 uses a 32-bit addressing scheme and supports over 4.3 billion devices. This may sound like a huge number but apparently, this is not enough. Due to the rapid increase in the use of the Internet, personal computers, smartphones and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, there will be a massive requirement for more IP addresses.
2. NAT technology reduces network performance.
At present, the limited address solution is NAT, network address translation technology. NAT is to turn multiple intranet hosts into a public IP to connect to the Internet. Although this can temporarily solve the problem of addressing shortages, it will bring more problems. Address translation puts great pressure on equipment, which will inevitably reduce network performance, increase delay and reduce the experience.
3. NAT can’t solve the address shortage problem thoroughly.
Because NAT realizes that a public network address carries multiple users’ traffic, the port number is used to distinguish the connections of different users, but a public network IP has only 65,535 ports at most, so the number of connections carried is limited. As user data continues to increase, more public IPs must be used.
Nowadays, with the rapid development of mobile Internet and the increasing data flow, it is urgent to grade IPv6, which is why several large Internet companies have taken the lead in IPv6 transformation.
4. Unable to adapt to the development of the Internet of Things
Everything is interconnected, and everything needs IP addresses. Of course, IPv4 is powerless. Today, the number of networked devices in the world has exceeded the world’s population. In the next few years, billions of devices such as automobiles, televisions, digital set-top boxes, electric meters, cameras, medical and health care, etc. will be connected to the network.
5. The existence of a broadcast mechanism will cause a loss of network performance.
The necessary protocols such as ARP and DHCP in IPv4 are broadcast, which will consume the performance of the network.
How does IPv6 solve these problems?
1. How does IPv6 solve these problems?
IPv6 uses 128-bit addressing and supports over 340 trillion trillion. Theoretically, the number of addresses is almost unlimited, and IPv6 can assign one address to every grain of sand on the earth.
2. Improve network performance
IPv6 can not only avoid the performance loss caused by NAT but also simplify the header structure and make data forwarding more efficient.
Compared with the IPv4 header, the IPv6 header removes IHL, identifiers, Flags, Fragment Offset, Header Checksum, Options, Padding fields, and only adds flow label fields, so the processing of the IPv6 header is greatly simplified compared with IPv4, and the processing efficiency is improved.
Of course, you may ask, these fields in the IPv6 header are all useful. What if you don’t have it when you need it? IPv6 puts forward the concept of an extended header, which can expand the header field as needed and realize the required functions. For example, if you need to do IP fragmentation, you can add the extension header for fragmentation.
In addition, IPv6 cancels the broadcast mechanism and replaces IPv4 broadcast with multicast, which can reduce the performance consumption of broadcast messages on the whole network. The specific principle will be explained in detail later.
3. Simplified operation and maintenance, automatic addressing
IPv4 needs DHCP to realize the terminal’s automatic address acquisition. IPv6 itself has the ability to automatically configure addresses.
4. More secure
IPv6 natively supports the IPsec extension header, which can ensure the security of data transmission from all aspects. Therefore, we can also find that OSPF and VRRP in IPv4 have to consider how to ensure their own security, and have joined the neighbor verification mechanism, while OSPFv3 and VRRP for IPv6 in IPv6 versions have no design verification mechanism because IPv6 itself can achieve security.